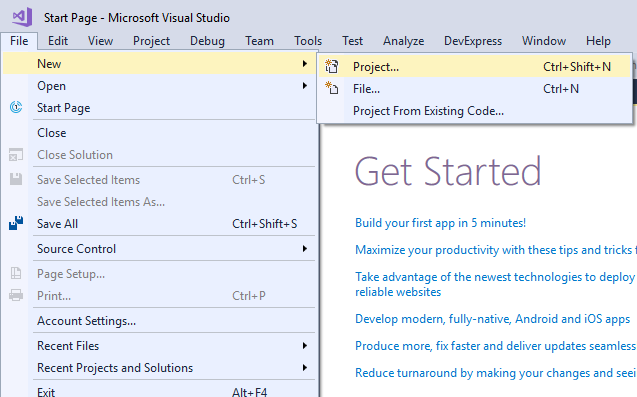
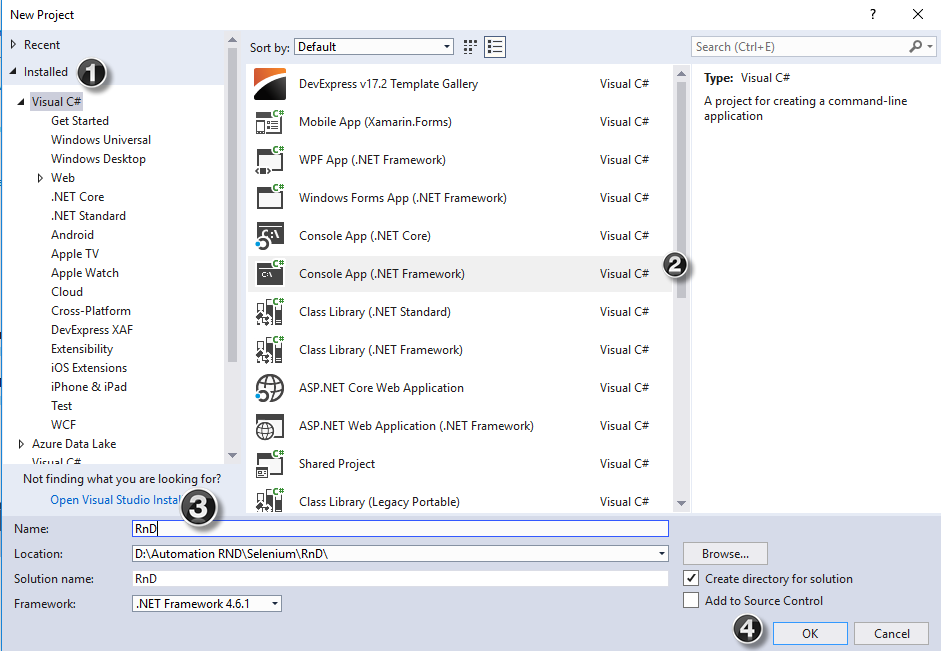
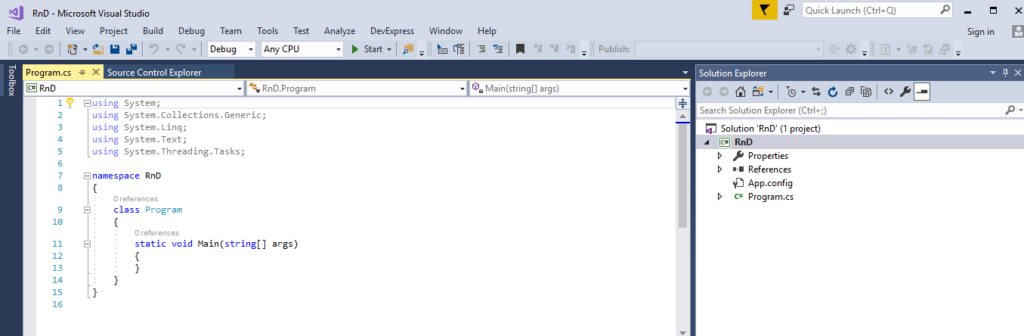
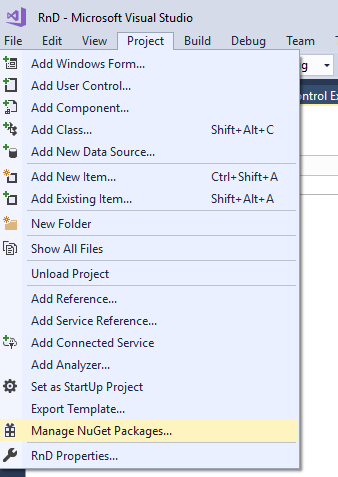
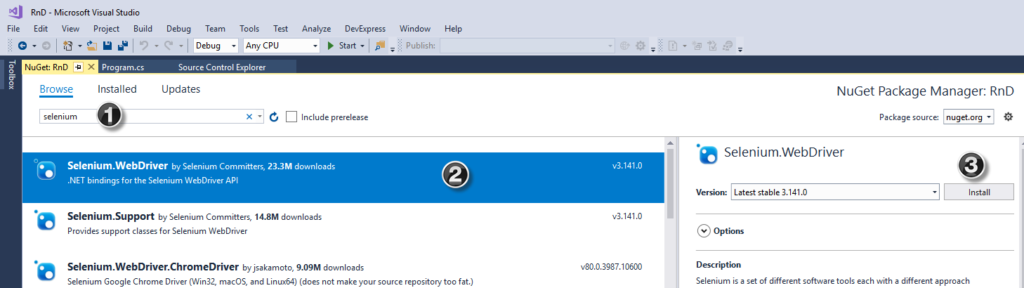
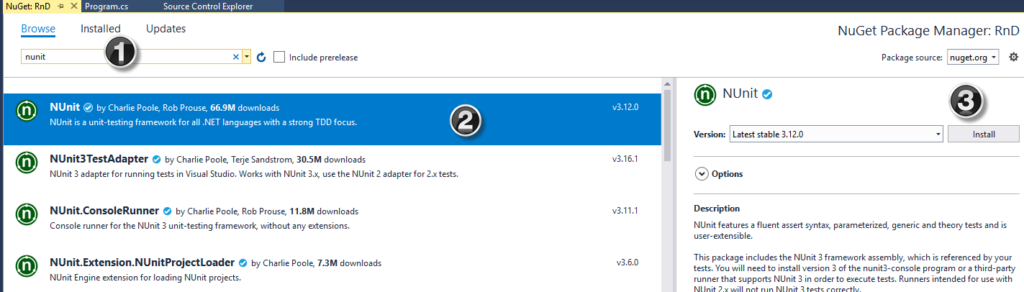
🧩 Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is everywhere — from writing code snippets to generating test cases, fixing bugs, and even suggesting architectural patterns. Developers use tools like ChatGPT, Copilot, and Tabnine every day to save time and effort. Yet, most developers will tell you — they still don’t fully trust AI.
Why? Because AI can follow instructions, but it doesn’t understand reality. It can tell you how to go to the fourth floor of a building — but if there are no stairs between the second and third, it won’t know you can’t get there.
This simple analogy reveals a deeper truth: AI doesn’t see, imagine, or reason like humans. It predicts. And that’s why developers treat AI as a helper, not a decision-maker.
⚙️ What AI Actually Does
AI doesn’t think; it calculates.
When you ask AI a question, it doesn’t know the answer — it predicts the most likely words that should come next based on patterns it has seen before.
For example:
🏢 If you ask, “How can I reach the fourth floor?”
AI might answer: “Take the stairs or elevator.”
But if your building doesn’t have stairs between the second and third floor, AI won’t know. It doesn’t understand the building; it only understands the pattern of what most buildings look like.
That’s how it works with code too. AI can predict what a “Login API test case” looks like because it has seen thousands of similar examples. But if your API has a custom authentication token logic or unique workflow, AI might fail completely.
🧠 Developers Trust Logic, Not Guesswork
Software developers — and QA engineers like us — live by logic. Every line of code has a reason, every test has an expected result.
AI, on the other hand, doesn’t explain why. It just gives you an answer that sounds right.
For instance:
- AI might generate a test case for a “Forgot Password” function.
- But it may miss verifying email token expiry time or invalid token reuse — things only a human tester would think of.
This lack of contextual reasoning makes developers cautious.
🎨 Creativity: The One Thing AI Still Can’t Imitate
AI can produce, but it can’t create.
When a developer faces a new problem — say, designing a unique caching strategy or optimizing load times under unusual network constraints — AI struggles because it depends on existing data.
Creativity isn’t about patterns. It’s about breaking patterns when they no longer work.
AI can paint you a picture using past images.
But it can’t imagine a world that doesn’t yet exist.
That’s what makes human developers irreplaceable.
🔍 Real-World Understanding vs. Pattern Prediction
Developers often deal with messy, real-world systems — bugs caused by hardware, network latency, human behavior, or even business politics.
AI doesn’t experience these things. It doesn’t “know” what a late-night production issue feels like. It can’t sense when something “looks off” in a UI or when an error message feels confusing to a user.
A QA engineer, on the other hand, can feel those gaps — because we understand the user.
That empathy and intuition are beyond any AI model’s reach right now.
🧪 Why QA Engineers Are Especially Careful
As QA professionals, our job is to find what others miss.
If we depend blindly on AI, we’ll miss the very things AI can’t see.
For example:
- AI might mark a test as “passed” because it matches the expected output.
- But a human tester notices the button color changed — a minor UI bug that affects usability.
AI doesn’t know what feels right; it only knows what looks correct statistically.
That’s why smart QA engineers use AI for speed — but keep human judgment for quality.
🧭 The Real Role of AI in Software Development
AI is not a replacement; it’s an enhancement.
It accelerates routine tasks, generates documentation, and helps you brainstorm.
But the responsibility — the final decision — must remain human.
Here’s how most experienced teams use AI safely:
- Code generation: AI drafts snippets; humans review and optimize.
- Test case creation: AI suggests scenarios; QA verifies coverage and adds edge cases.
- Bug triage: AI clusters similar issues; humans prioritize based on business impact.
It’s collaboration — not automation.
🧱 The “Fourth Floor” Lesson for Developers
Let’s go back to your building analogy.
Imagine AI as a smart assistant standing at the front gate. You ask, “How can I reach the fourth floor?”
It answers, “Take the stairs.”
But you know there’s no stairway from floor two to three.
If you blindly follow AI, you’ll get stuck.
If you think critically, you’ll redesign the staircase.
That’s the essence of why developers don’t fully trust AI — not because AI is wrong, but because AI doesn’t know when it’s wrong.
🌍 Conclusion: Trust Requires Understanding
AI is brilliant at prediction, not perception. It’s fast, but it lacks awareness.
Developers and testers thrive on logic, experience, and creativity — the very qualities AI can’t replicate.
The future isn’t about AI replacing developers; it’s about developers who know how to use AI wisely.
AI can help you reach the fourth floor faster — but only if you’ve already built the stairs.