Automation is transforming the software development process—making testing faster, reducing repetitive tasks, and improving productivity. In this guide, we’ll explore how to automate web browsers using Selenium with C# inside Visual Studio Code, and more specifically, how to boost your workflow using the Cursor AI assistant (v1.1.5).
🧠 Cursor is an AI-powered coding assistant embedded directly into VS Code. It helps write, explain, and debug code faster using natural language prompts.
🔧 Prerequisites
Before diving in, make sure the following tools are installed:
- .NET SDK (6.0 or later) – Download
- Visual Studio Code (v1.96.2 or later) – Download
- Cursor AI extension (v1.1.5) – Installed from https://www.cursor.so/
- Google Chrome and ChromeDriver
- NuGet packages for Selenium
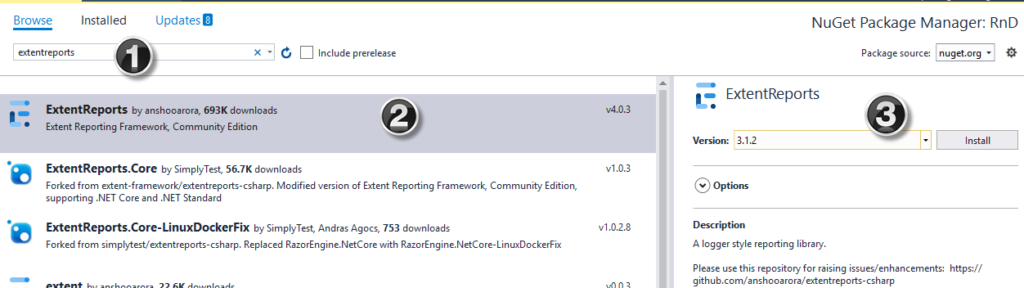
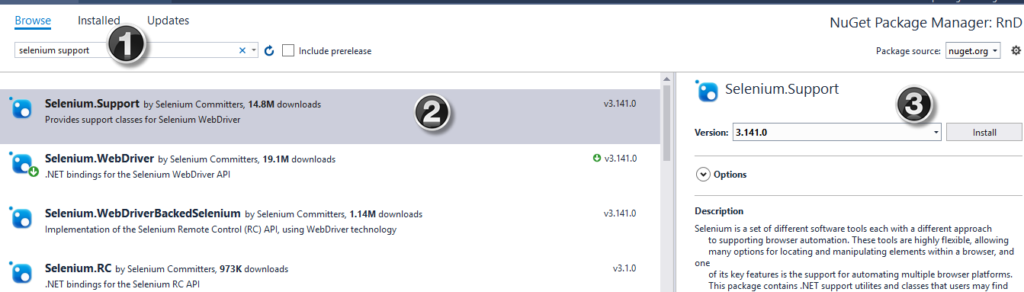
🚀 Step 1: Create a New C# Project with Cursor
Open VS Code with Cursor enabled and type:
dotnet new console -n SeleniumAutomation
cd SeleniumAutomationAsk Cursor:
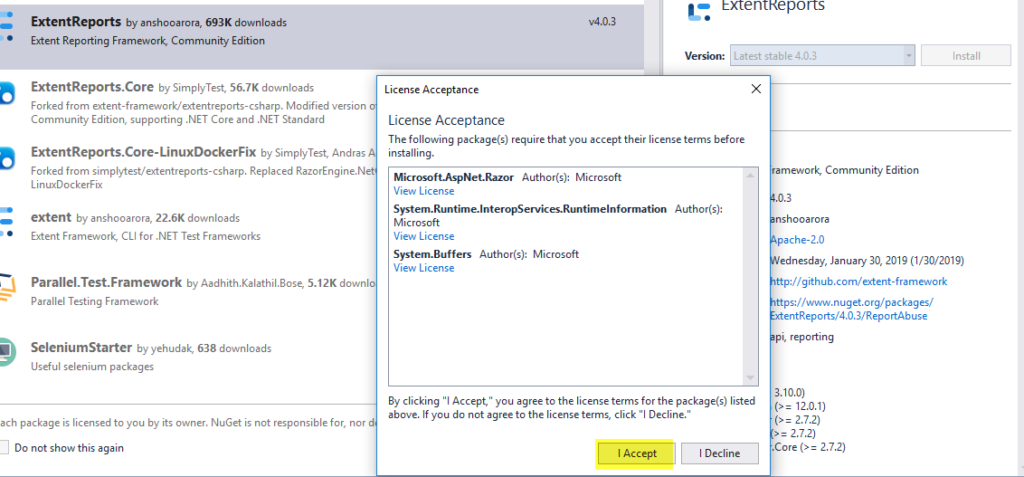
💬 “Add Selenium dependencies to this C# project using NuGet.”
It will auto-generate the correct command:
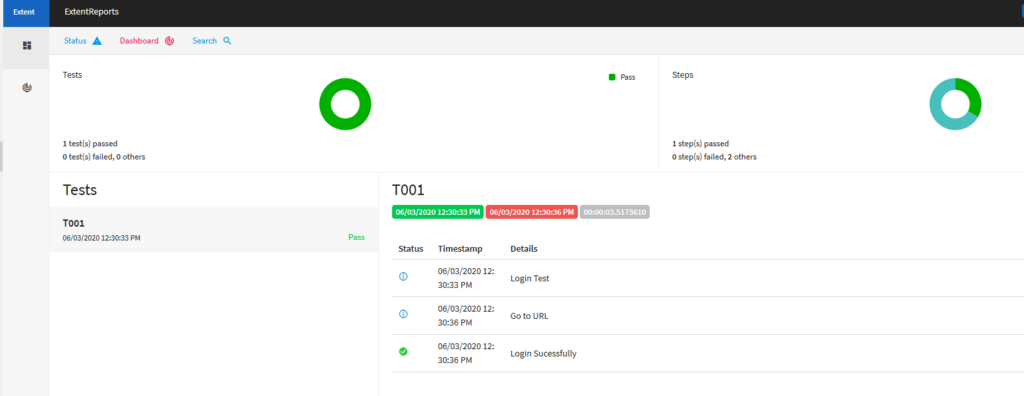
💻 Step 2: Automate a Browser Using Selenium
Open Program.cs, and type this prompt into Cursor:
💬 “Create a sample Selenium script in C# that opens Chrome, searches on Google, and closes the browser.”
Cursor will generate code similar to this:
using OpenQA.Selenium;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Chrome;
using System;
using System.Threading;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
using var driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.Navigate().GoToUrl("https://www.google.com");
var searchBox = driver.FindElement(By.Name("q"));
searchBox.SendKeys("Selenium with C#");
searchBox.SendKeys(Keys.Enter);
Thread.Sleep(3000);
driver.Quit();
}
}
🧠 Step 3: Debug & Explain with Cursor
Highlight any part of your code and ask:
💬 “Explain this line.”
💬 “How can I wait until the element is visible?”
💬 “Convert this to useWebDriverWait.”
Cursor will rewrite or enhance the logic with contextual explanations.
🖱 Bonus: Automating Actions via JavaScript
Want to simulate mouse interaction or click buttons? Try:
IJavaScriptExecutor js = (IJavaScriptExecutor)driver;
js.ExecuteScript("document.querySelector('input[name=q]').click();");
You can prompt Cursor:
💬 “Use JavaScriptExecutor to click a button by CSS selector.”
You can prompt Cursor:
💬 “Use JavaScriptExecutor to click a button by CSS selector.”
🧪 Cursor for Test Automation Engineers
Cursor can also:
- Suggest NUnit test structure
- Generate test classes from comments
- Refactor repeated Selenium actions into reusable methods
- Provide answers from docs directly in VS Code
✅ Benefits of Using Cursor with Selenium in VS Code
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Code generation | Faster setup of boilerplate Selenium scripts |
| Auto-debugging | Fixes C# errors and Selenium exceptions instantly |
| Natural language support | Reduces context switching—write code by asking |
| Seamless integration | Stays inside VS Code, no need for external tools |
🧩 Conclusion
Combining Selenium, C#, and Cursor AI inside VS Code creates a supercharged automation workflow. Whether you’re a QA engineer or a developer, this setup will save hours, reduce complexity, and allow you to test smarter—not harder.